Design Thinking 101: what SaaS companies can learn from design sprints
There’s been a lot of hype in the tech world around design thinking.

Mas o que é o design thinking? E o que podemos aprender com ele?
Melhor ainda, como as empresas de SaaS podem usá-lo e implementá-lo?
Let’s get started! 👇
Então, o que é exatamente o design thinking?
Em poucas palavras, o design thinking é uma abordagem iterativa e flexível que se concentra em entender melhor os usuários por meio do design e da colaboração.
It’s all about putting forward ideas that emphasize how your users think and behave.
Design thinking allows your team to explore real issues that real users want to solve. 🙌
E você pode fazer isso por meio de uma série de iterações e prototipagem que, em última análise, trazem atualizações para seu(s) produto(s) que deixam seus clientes satisfeitos.

Esse processo também permite que sua empresa encontre soluções ou estratégias alternativas que talvez não estivessem inicialmente previstas no projeto original.
Como você já deve ter percebido, o design thinking tem tudo a ver com os usuários, ou clientes, de um produto. Ele é construído com empatia em mente.
Because, after all, some of the best products out there today are also some of the most human-centric products as well. 👫
Since it’s a collaborative process and is intended to be iterative, there is quite a bit of brainstorming, prototyping and testing involved.
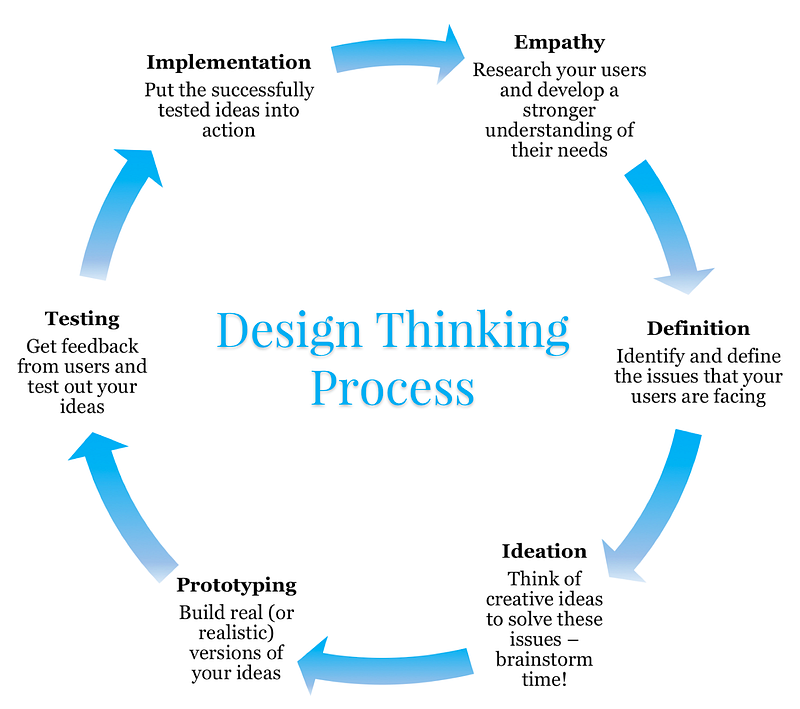
What is the design thinking process?
With all of these different aspects of design thinking, it’s easy to get confused or get a little lost. 🙇
Mas, definitivamente, tenha em mente que há várias maneiras diferentes de rotular esse processo, e muitos recursos terão nomes diferentes para essas etapas, mas a execução de cada etapa ainda está intacta.
Você pode pensar no processo em três fases abrangentes: Compreender, Explorar e Materializar.
So let’s break it down step by step.
Understanding the user
Empatia
First thing’s first: you need to better understand your users.
Empathy is a major part of design thinking — because it’s the key to thinking of human-centric solutions. 💛
Pesquise, observe e até mesmo entreviste seus usuários. Coloque-se no lugar deles.
Try to figure out what they want or some of the problems they’re trying to solve in their daily lives, what motivates them and how they experience your company — then try to figure out como sua empresa facilita a vida deles.

It’s important to put your own assumptions and biases aside and really try to gain insights into how your users think and feel.
And while the amount of time you should spend on this step greatly depends on your own time constraints, do your best to gather as much information possible before moving to the next step. ➡
Os sprints no design thinking são melhores se durarem cerca de uma semana no total, embora algumas empresas prefiram sprints de duas semanas.
Quanto mais informações você reunir, melhor poderá entender seus usuários e suas necessidades.
Definição
Com base em todas as excelentes informações coletadas na primeira etapa, agora você pode começar a identificar e definir os problemas que deseja resolver para seus usuários.
Analyze and then synthesize these findings in order to get to the core of what your users want — this usually comes in the form of a human-centric problem statement.
These problem statements combine three elements — user, need, insight — and turn them into addressable questions to tackle. 🤔
Exemplos de declarações de problemas:
- Como podemos ajudar os usuários a se integrarem mais rapidamente?
- Como podemos tornar nosso atendimento ao cliente mais eficiente?
- Como podemos tornar nossos guias de instruções mais interessantes?
Essas declarações de problemas tornam o processo de ideação (nossa próxima etapa) muito mais claro.
It also makes it easier to define the how rather than just the why — which helps you get to the heart of users’ needs.
Exploring possibilities for your users
Ideação
Now that you’ve determined the things you want to tackle, this stage is where you start to come up with ideas. 😁
You now better understand your users thanks to the Empathy stage, and you’ve identified what you’d like to solve in the Definition stage, so now it’s time to figure out how you’re going to make it happen.

Há muitas maneiras de realizar essa etapa, pois há métodos que vão desde o Brainstorm até a Pior Ideia Possível e SCAMPER.
Use what your team prefers, or what you feel will help you find the best solutions. It’s even better if you use a mix of methods during this step.
Gather as many ideas as possible in the beginning, then start to discuss and determine which ones you’d like to try out.
Prototipagem
It’s now time to produce examples of your ideas!
Prototyping is the opportunity for your team to create stripped-down, inexpensive versions of the products/features you want to test. 💪
Isso permite que a sua equipe explore as soluções encontradas no estágio anterior de uma forma mais tangível.

Depois de criados, os protótipos podem ser testados dentro da equipe ou com outro departamento da empresa para determinar as melhores soluções possíveis que surgiram nas primeiras etapas do processo.
At this point, your team can determine whether each idea is accepted, rejected or improved and re-evaluated. ✅
Para passar para a próxima etapa, a equipe deve ter uma ideia melhor das restrições e dos problemas do produto/recurso, a fim de informar melhor como os usuários reais provavelmente se sentirão com a versão final.
Materializing your ideas for users
Testes
Once the best ideas are determined from the prototyping phase, it’s time to test them!
Obtenha feedback do usuário, monitor any changes in engagement or usage of your product/feature and try to determine how much this change has improved the experience of your users. 😍
It’s entirely possible that you will continue to make improvements as you start to get user feedback — the process is designed so that you can iterate and adapt as needed throughout.
Implementação
Finally, once you’ve successfully tested your new product/feature, it’s time to officially implement it as a permanent addition to your company.

The things you address for your users during this process can always be revisited if another problem arises. It’s a cycle — so the quest for a better user experience can continue as much as you see fit.
What are we supposed to learn from this?
We’ve touched on the fact that design thinking uses empathy to better understand your users, but it also helps you reinforce the feedback loop.
By empowering your users to give more feedback and try out more new features or products, it makes them feel seen and listened to, and it makes for happier, more satisfied customers in the end. 🤗
How could this apply to SaaS?
Design thinking can be applied to a variety of industries and organizations — including within SaaS companies. 👍
Perhaps you’re feeling stuck on how to make your onboarding process more streamlined?
Or maybe there’s a particular new feature you aren’t sure how to implement?
O design thinking pode resolver esses problemas e muitos outros.

Isso não só permite que sua empresa estabeleça mais confiança entre você e seus usuários atuais e mais credibilidade entre você e os clientes em potencial, mas também ajuda sua empresa a pensar um pouco fora da caixa.
Once you remove yourself mentally (and emotionally) as an employee and really put yourself in the shoes of the user, you’re able to have a clearer vision of what needs to be improved or created in order to make your users have the best experience possible. 🤟
A experiência do usuário pode, às vezes, ser deixada de lado na criação de uma empresa.
There are so many other things to think about — administration, staffing, building the actual tech around the product, marketing, etc. so it can sometimes lead to a lack of empathy toward your users. 😓
Don’t do that.
Instead, think about the things your users are giving you feedback on (and if you aren’t collecting any type of feedback, get on that right now) and start to think about what you can do to tackle their issues.
Whether it’s offering clear, visual data or a navigation that makes sense, design is a crucial part of a product’s success — so make sure you’re giving them the best possible product, both in terms of tech and in terms of usability.
OK, I want to try this with my company. How do I get started?
There is a vast amount of knowledge and resources on design thinking available online — yes, surprising, I know. 😅
But really the first thing you should do to get started is to discuss with your team that you’d like to try this method and have everyone “buy into” design thinking.
That’s not to say that you’re trying to sell them snake oil or are asking them to join a cult, but it’s important for your team to be in the right mindset when trying to learn from users.
Design thinking sprints can take a lot of creative thinking and requires the ability to have an open mind — so it’s good to at least give them a head’s up about the purpose and process.

Um ótimo recurso para ajudar você e sua equipe a aprender mais sobre o próprio design thinking é Stanford D.School: A Virtual Crash Course in Design Thinking, mas, conforme mencionado, há muitos por aí.
If you’re interested in trying design sprints with your team, there’s an excellent Google Ventures page all about design sprints and some resources to help get you started as well.
Happy design thinking! 🤘
Esperamos que você tenha gostado desta postagem. Se gostou, espalhe a notícia!
Para obter mais informações importantes sobre startups, marketing de crescimento e vendas:
- 22+ melhores podcasts de vendas que você deve conferir em 2024 - dezembro 21, 2023
- Scripts de chamadas frias para seres humanos reais - 21 de setembro de 2023
- As 25+ melhores ferramentas de vendas para ajudar sua equipe a ser bem-sucedida - agosto 10, 2023