Design Thinking 101: what SaaS companies can learn from design sprints
There’s been a lot of hype in the tech world around design thinking.

Ma che cos'è il pensiero progettuale? E cosa possiamo imparare da esso?
Meglio ancora, come possono utilizzarlo e implementarlo le aziende SaaS?
Let’s get started! 👇
Quindi, cos'è esattamente il design thinking?
In poche parole, il design thinking è un approccio iterativo e flessibile che si concentra su una migliore comprensione degli utenti attraverso la progettazione e la collaborazione.
It’s all about putting forward ideas that emphasize how your users think and behave.
Design thinking allows your team to explore real issues that real users want to solve. 🙌
E potete farlo attraverso una serie di iterazioni e prototipi che alla fine portano aggiornamenti ai vostri prodotti che rendono felici i vostri clienti.

Questo processo consente inoltre alla vostra azienda di trovare soluzioni o strategie alternative che potrebbero non essere emerse dal progetto originale.
Come avrete già notato, il design thinking si concentra sugli utenti, o clienti, di un prodotto. È costruito tenendo conto dell'empatia.
Because, after all, some of the best products out there today are also some of the most human-centric products as well. 👫
Since it’s a collaborative process and is intended to be iterative, there is quite a bit of brainstorming, prototyping and testing involved.
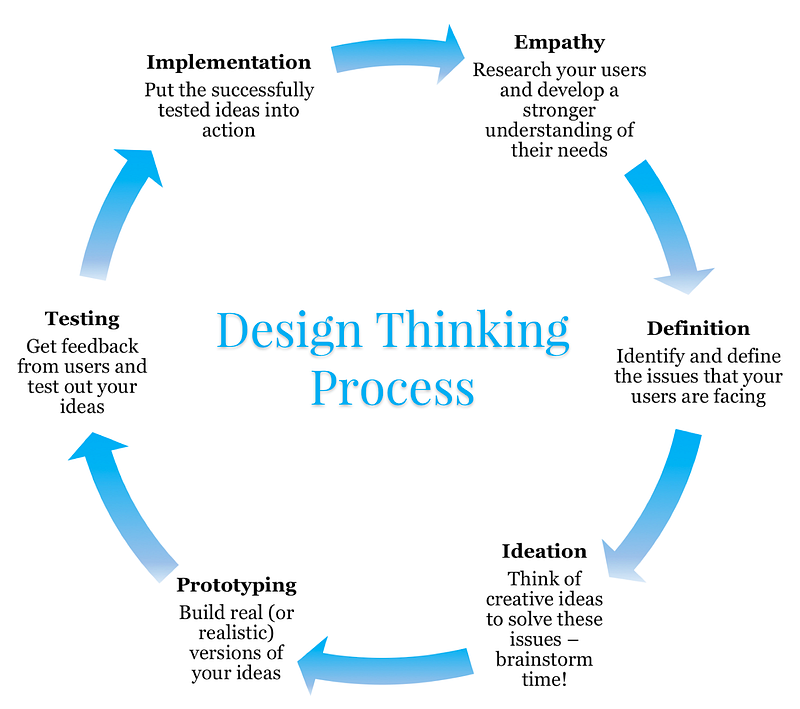
What is the design thinking process?
With all of these different aspects of design thinking, it’s easy to get confused or get a little lost. 🙇
Tenete però presente che esistono diversi modi di etichettare questo processo e che molte risorse avranno nomi diversi per questi passaggi, ma l'esecuzione di ogni fase rimane intatta.
Si può pensare al processo in tre fasi generali: Comprendere, Esplorare e Realizzare.
So let’s break it down step by step.
Understanding the user
L'empatia
First thing’s first: you need to better understand your users.
Empathy is a major part of design thinking — because it’s the key to thinking of human-centric solutions. 💛
Fate ricerche, osservate e intervistate i vostri utenti. Mettetevi nei loro panni.
Try to figure out what they want or some of the problems they’re trying to solve in their daily lives, what motivates them and how they experience your company — then try to figure out come la vostra azienda semplifica loro la vita.

It’s important to put your own assumptions and biases aside and really try to gain insights into how your users think and feel.
And while the amount of time you should spend on this step greatly depends on your own time constraints, do your best to gather as much information possible before moving to the next step. ➡
Gli sprint nel design thinking sono migliori se durano circa una settimana in totale, anche se alcune aziende preferiscono sprint di due settimane.
Più informazioni si raccolgono, meglio si possono capire gli utenti e le loro esigenze.
Definizione
Sulla base di tutte le informazioni raccolte nella prima fase, potete ora iniziare a identificare e definire i problemi che volete risolvere per i vostri utenti.
Analyze and then synthesize these findings in order to get to the core of what your users want — this usually comes in the form of a human-centric problem statement.
These problem statements combine three elements — user, need, insight — and turn them into addressable questions to tackle. 🤔
Esempi di dichiarazioni di problemi:
- Come possiamo aiutare gli utenti a salire a bordo più velocemente?
- Come possiamo rendere più efficiente il nostro servizio clienti?
- Come possiamo rendere le nostre guide più interessanti?
Queste dichiarazioni sul problema rendono molto più chiaro il processo di ideazione (la fase successiva).
It also makes it easier to define the how rather than just the why — which helps you get to the heart of users’ needs.
Exploring possibilities for your users
Ideazione
Now that you’ve determined the things you want to tackle, this stage is where you start to come up with ideas. 😁
You now better understand your users thanks to the Empathy stage, and you’ve identified what you’d like to solve in the Definition stage, so now it’s time to figure out how you’re going to make it happen.

Ci sono molti modi per affrontare questa fase, come ci sono metodi che vanno da Brainstorm a Worst Possible Idea a SCAMPER.
Use what your team prefers, or what you feel will help you find the best solutions. It’s even better if you use a mix of methods during this step.
Gather as many ideas as possible in the beginning, then start to discuss and determine which ones you’d like to try out.
Prototipazione
It’s now time to produce examples of your ideas!
Prototyping is the opportunity for your team to create stripped-down, inexpensive versions of the products/features you want to test. 💪
Questo permette al team di esplorare le soluzioni proposte nella fase precedente in modo più tangibile.

Una volta creati, i prototipi possono essere testati all'interno del team o con un altro reparto dell'azienda per determinare le migliori soluzioni possibili emerse dalle prime fasi del processo.
At this point, your team can determine whether each idea is accepted, rejected or improved and re-evaluated. ✅
Per passare alla fase successiva, il team dovrebbe avere un'idea più precisa dei vincoli e dei problemi del prodotto/caratteristica, in modo da informarsi meglio su come gli utenti reali si sentiranno probabilmente con la versione finale.
Materializing your ideas for users
Test
Once the best ideas are determined from the prototyping phase, it’s time to test them!
Raccogliere il feedback degli utenti, monitor any changes in engagement or usage of your product/feature and try to determine how much this change has improved the experience of your users. 😍
It’s entirely possible that you will continue to make improvements as you start to get user feedback — the process is designed so that you can iterate and adapt as needed throughout.
Attuazione
Finally, once you’ve successfully tested your new product/feature, it’s time to officially implement it as a permanent addition to your company.

The things you address for your users during this process can always be revisited if another problem arises. It’s a cycle — so the quest for a better user experience can continue as much as you see fit.
What are we supposed to learn from this?
We’ve touched on the fact that design thinking uses empathy to better understand your users, but it also helps you reinforce the feedback loop.
By empowering your users to give more feedback and try out more new features or products, it makes them feel seen and listened to, and it makes for happier, more satisfied customers in the end. 🤗
How could this apply to SaaS?
Design thinking can be applied to a variety of industries and organizations — including within SaaS companies. 👍
Perhaps you’re feeling stuck on how to make your onboarding process more streamlined?
Or maybe there’s a particular new feature you aren’t sure how to implement?
Il design thinking può risolvere questi problemi e molti altri.

Non solo permette alla vostra azienda di stabilire una maggiore fiducia tra voi e i vostri utenti attuali e una maggiore credibilità tra voi e i potenziali clienti, ma aiuta anche la vostra azienda a pensare un po' fuori dagli schemi.
Once you remove yourself mentally (and emotionally) as an employee and really put yourself in the shoes of the user, you’re able to have a clearer vision of what needs to be improved or created in order to make your users have the best experience possible. 🤟
L'esperienza dell'utente può talvolta passare in secondo piano quando si costruisce un'azienda.
There are so many other things to think about — administration, staffing, building the actual tech around the product, marketing, etc. so it can sometimes lead to a lack of empathy toward your users. 😓
Don’t do that.
Instead, think about the things your users are giving you feedback on (and if you aren’t collecting any type of feedback, get on that right now) and start to think about what you can do to tackle their issues.
Whether it’s offering clear, visual data or a navigation that makes sense, design is a crucial part of a product’s success — so make sure you’re giving them the best possible product, both in terms of tech and in terms of usability.
OK, I want to try this with my company. How do I get started?
There is a vast amount of knowledge and resources on design thinking available online — yes, surprising, I know. 😅
But really the first thing you should do to get started is to discuss with your team that you’d like to try this method and have everyone “buy into” design thinking.
That’s not to say that you’re trying to sell them snake oil or are asking them to join a cult, but it’s important for your team to be in the right mindset when trying to learn from users.
Design thinking sprints can take a lot of creative thinking and requires the ability to have an open mind — so it’s good to at least give them a head’s up about the purpose and process.

Una grande risorsa per aiutare voi e il vostro team a saperne di più sul design thinking è Stanford D.School: A Virtual Crash Course in Design Thinking, ma come detto, ce ne sono tantissimi in giro.
If you’re interested in trying design sprints with your team, there’s an excellent Google Ventures page all about design sprints and some resources to help get you started as well.
Happy design thinking! 🤘
Speriamo che questo post vi sia piaciuto. Se vi è piaciuto, spargete la voce!
Per ulteriori informazioni su startup, growth marketing e vendite:
- 22+ Best Sales Podcasts You Should Check Out in 2024 - 21 Dicembre 2023
- Scritture di chiamata a freddo per esseri umani reali - 21 settembre 2023
- Gli oltre 25 migliori strumenti di vendita per aiutare il vostro team ad avere successo - 10 Agosto 2023